
This particular EQ divides the frequency range (20Hz-20kHz) into ten different bands. Although the number of bands can vary, the graphic EQ in the VS recorder is typically a 10-band EQ. Once located, adjust the gain appropriately.Ī graphic equalizer is primarily used for live mixing.

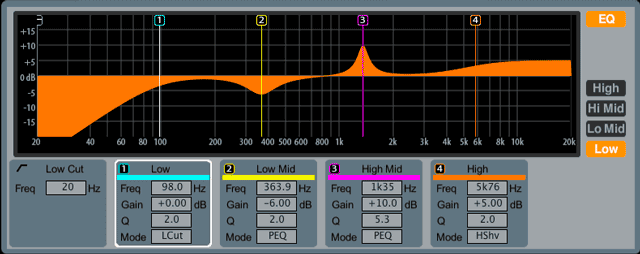
Therefore, increasing the gain (+12 on the VS) in a band where you think the desired frequency might be, and then browsing through the frequencies (sweeping), will help you identify which one is the desired one. If there is a Q, Gain, and Freq setting, the EQ is called a fully parametric EQ.Ī sweepable EQ is a great tool to have because its not always easy to find the desired frequency for a particular instrument, whether you want to cut or boost. The Q is the width of the area around the selected frequency that will be affected by the changes in gain. When adjusting the parametric EQ settings on the VS recorders, there is a gain and frequency setting for the Low and High frequency bands Theres an additional Q setting for the Low-Mid and Hi-Mid bands. With this type of EQ the frequency range is separated into 4 different segments, or bands, of frequencies: Low, Low-Mid, Hi-Mid, High. You can change a bands gain and frequency values on the interactive EQ display with your mouse by dragging its triangle.Ī parametric equalizer is the most flexible type of sweepable EQ because it can freely change the cutoff frequency, or the bandwidth (Q). Theres an interactive display that shows you the settings of the four band of EQs. As a default setting, the EQ in the channel is turned off. In each of the CH EDIT screens, you can see the channels current EQ settings presented in graphic form, and can turn all of the channels EQ bands on or off with a single switch. When this concept is applied to the entire recording, the end result is a well blended mix where the individual instruments can be heard and understood. This way we can focus on the sweet spots of the different instruments and reduce the extraneous material that distorts the clarity of the mix.

For example, if we cut at 300Hz on the bass guitar to reduce some of the muddiness and give it some clarity, then we may want to boost the EQ at 300Hz on the electric guitar. Ideally, EQ is used to give each instrument its own identity in the mix, or in the frequency range. Equalization is the process of manipulating the frequency content of an audio signal in order to change its tonal quality.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
